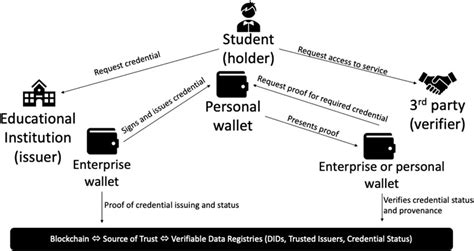
In the digital age, the concept of identity has evolved beyond traditional paper documents. With the rise of blockchain technology, there’s a growing debate on the future of digital identity sovereignty. This article aims to explore the contrasting approaches of blockchain-based digital identities and government-issued ID systems, highlighting their respective strengths and weaknesses.
Blockchain: A New Frontier in Digital Identity

Blockchain technology, known for its decentralized and immutable nature, has the potential to revolutionize the way we manage digital identities. By leveraging the power of blockchain, individuals can gain more control over their personal information, ensuring its security, privacy, and authenticity.
1. Decentralization: Blockchain-based digital identities eliminate the need for centralized authorities, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Instead, individuals hold their own identity data on a decentralized network, ensuring greater security and privacy.
2. Transparency: The immutable nature of blockchain allows for a transparent and auditable record of identity transactions. This transparency can help build trust among individuals and organizations, as they can verify the authenticity of someone’s identity without relying on third-party intermediaries.
3. Interoperability: Blockchain can facilitate the creation of a universal digital identity standard that can be used across different platforms and services. This interoperability can streamline identity verification processes and reduce the burden of maintaining multiple identities.
Government-Issued ID Systems: The Traditional Approach
Government-issued ID systems have been in place for decades, providing a standardized means of verifying individuals’ identities. However, these systems face several challenges in the digital age, including data breaches, privacy concerns, and the need for continuous innovation.
1. Centralization: Government-issued ID systems are centralized, making them vulnerable to data breaches and unauthorized access. When a single authority holds vast amounts of personal information, the risk of misuse is heightened.
2. Privacy Concerns: Government-issued ID systems often collect and store sensitive personal information, raising privacy concerns. The potential for misuse or unauthorized disclosure of this information is a significant risk.
3. Reliability: Traditional ID systems rely on physical documents, such as passports and driver’s licenses, which can be lost, stolen, or damaged. This makes it difficult for individuals to prove their identity in real-time.
The Future of Digital Identity Sovereignty
The debate between blockchain-based digital identities and government-issued ID systems centers on the concept of digital identity sovereignty. On one hand, blockchain technology empowers individuals to take control of their personal information, ensuring its security and privacy. On the other hand, government-issued ID systems provide a standardized and regulated approach to identity management.
The future of digital identity sovereignty may lie in a hybrid model that combines the strengths of both approaches. This hybrid model could leverage blockchain technology to enhance the security and privacy of personal data, while maintaining the regulatory oversight and standardized processes provided by government-issued ID systems.
In conclusion, the choice between blockchain and government-issued ID systems in the context of digital identity sovereignty is not an either/or situation. Instead, a balanced and innovative approach that incorporates the best of both worlds is necessary to ensure a secure, private, and efficient digital identity ecosystem.