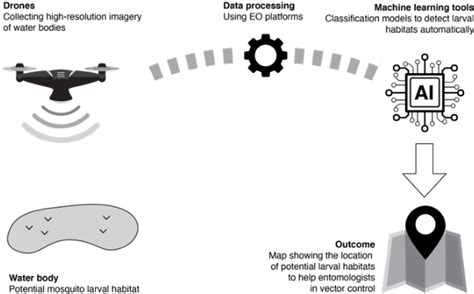
In the year 2028, the landscape of malaria prediction and control has been revolutionized by the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and satellite technology. This article delves into how AI-driven satellite mosquito habitat mapping has significantly enhanced the accuracy of malaria prediction, offering a glimpse into the future of disease surveillance.
**The Evolution of Malaria Prediction**

Malaria, a mosquito-borne infectious disease, has been a persistent threat to global health for centuries. Traditional methods of predicting malaria outbreaks were often based on historical data and expert opinions, which were time-consuming and prone to human error. However, with the advent of AI and satellite imagery, these methods have become more efficient and accurate.
**AI and Satellite Imagery: A Match Made in Heaven**
The integration of AI with satellite imagery has opened new avenues in the field of disease prediction. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from satellite images to identify potential mosquito habitats, which are the breeding grounds for malaria-carrying mosquitoes.
**How AI Enhances Accuracy**
1. **Data Analysis**: AI algorithms are capable of processing and analyzing complex data sets, including satellite images, weather patterns, and geographical information. This enables them to identify patterns and correlations that may not be apparent to human analysts.
2. **Real-Time Monitoring**: AI-driven satellite mosquito habitat mapping allows for real-time monitoring of potential mosquito breeding sites. This means that health authorities can take immediate action to prevent outbreaks before they occur.
3. **Predictive Modeling**: By utilizing historical data and real-time inputs, AI can create predictive models that forecast the likelihood of malaria outbreaks. These models can be refined over time as more data becomes available.
**The Role of Satellite Imagery**
Satellite imagery provides a comprehensive view of the Earth’s surface, allowing for the identification of various environmental factors that contribute to mosquito breeding. These factors include:
1. **Water Bodies**: Standing water is a breeding ground for mosquitoes, and satellite imagery can easily identify such areas.
2. **Vegetation**: Certain types of vegetation are more conducive to mosquito breeding than others, and AI can analyze satellite imagery to identify these conditions.
3. **Urbanization**: As urbanization increases, the risk of malaria outbreaks may also rise. AI-driven satellite imagery can help identify urban areas with high potential for mosquito breeding.
**The Future of Malaria Prediction**
The accuracy of AI-driven satellite mosquito habitat mapping has already begun to make a significant impact on malaria control efforts. As AI technology continues to evolve, we can expect even greater improvements in the accuracy and efficiency of malaria prediction.
1. **Early Detection and Intervention**: With enhanced accuracy, health authorities can detect and intervene in potential malaria outbreaks at an earlier stage, reducing the spread of the disease.
2. **Resource Allocation**: By identifying high-risk areas, resources can be allocated more effectively, ensuring that interventions are targeted where they are needed most.
3. **Global Collaboration**: AI-driven satellite mosquito habitat mapping can be shared across borders, enabling global collaboration in the fight against malaria.
In conclusion, the year 2028 marks a significant milestone in the battle against malaria. The integration of AI and satellite technology has revolutionized the way we predict and control malaria outbreaks, offering a promising future for global health. As we continue to refine these technologies, the world can look forward to a future where malaria is a thing of the past.