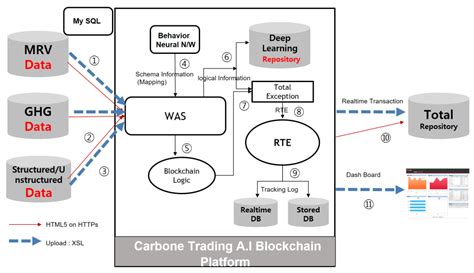
Introduction:
The global carbon trading market has been evolving rapidly, with blockchain technology emerging as a key enabler for enhancing transparency and efficiency. As we approach 2028, the integration of blockchain in carbon trading is expected to bring significant advancements in market transparency. This article explores the potential of blockchain in carbon trading and the role of global market transparency audits in ensuring a sustainable future.

I. The Rise of Blockchain in Carbon Trading
1. Decentralization and Transparency
Blockchain technology offers a decentralized and transparent platform for carbon trading. By eliminating intermediaries, it reduces costs and minimizes the risk of fraud, ensuring a fair and transparent market.
2. Smart Contracts
Smart contracts, a feature of blockchain, enable automated execution of agreements between parties. In carbon trading, smart contracts can facilitate the buying and selling of carbon credits, ensuring that transactions are executed promptly and accurately.
3. Enhanced Traceability
Blockchain’s inherent ability to record transactions in a tamper-proof manner enhances the traceability of carbon credits. This enables stakeholders to verify the authenticity and origin of carbon credits, promoting trust and transparency in the market.
II. Global Market Transparency Audits
1. Importance of Audits
Global market transparency audits play a crucial role in ensuring the integrity of the carbon trading market. These audits help verify the accuracy of carbon credits, assess the compliance of participants, and identify potential risks.
2. Role of Blockchain in Audits
Blockchain technology can significantly streamline the audit process by providing a transparent and immutable ledger of carbon credit transactions. This enables auditors to verify the authenticity and compliance of carbon credits more efficiently.
3. Benefits of Blockchain-based Audits
– Reduced Audit Costs: Blockchain-based audits can lower the costs associated with traditional auditing processes.
– Faster Auditing: The decentralized nature of blockchain allows for real-time verification of carbon credits, speeding up the auditing process.
– Enhanced Accuracy: The tamper-proof nature of blockchain ensures the accuracy of audit results.
III. Challenges and Future Outlook
1. Scalability and Interoperability
One of the main challenges in the integration of blockchain in carbon trading is scalability and interoperability. As the market grows, ensuring that blockchain platforms can handle large volumes of transactions without compromising on performance is crucial.
2. Regulatory Framework
The development of a robust regulatory framework is essential for the widespread adoption of blockchain in carbon trading. Governments and regulatory bodies need to collaborate to create a conducive environment for blockchain-based carbon trading.
3. Future Outlook
Despite the challenges, the potential of blockchain in carbon trading is immense. As the technology continues to evolve and regulatory frameworks are established, we can expect a more transparent, efficient, and sustainable carbon trading market by 2028.
Conclusion:
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the carbon trading market by enhancing transparency and efficiency. With the increasing importance of global market transparency audits, the integration of blockchain in carbon trading is set to bring significant advancements by 2028. As we move towards a more sustainable future, embracing blockchain technology will be crucial in ensuring the integrity and effectiveness of carbon trading.