In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, the concept of space-based data centers has garnered significant attention. As we approach 2028, the reliability of these centers, particularly in terms of radiation-hardened servers, becomes a critical factor in ensuring seamless operation and data integrity. This article delves into the challenges and advancements in radiation-hardened server technology that are shaping the future of space-based data centers.
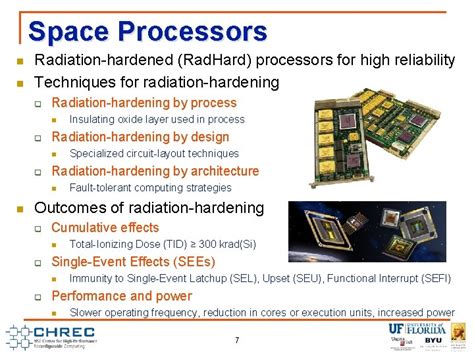
The Need for Radiation-Hardened Servers

Space-based data centers operate in an environment fraught with extreme conditions, including intense radiation. This radiation can be detrimental to traditional servers, leading to malfunctions and data corruption. To counter this challenge, the development of radiation-hardened servers has become a priority.
These servers are designed to withstand the harsh conditions of space, ensuring continuous operation and data integrity. The reliability of these servers is of paramount importance, as they are expected to process and store vast amounts of data for various applications, including satellite communication, global positioning systems, and space exploration missions.
Advancements in Radiation-Hardened Server Technology
Over the years, significant advancements have been made in the development of radiation-hardened server technology. These advancements have enabled servers to handle the extreme conditions of space with greater efficiency and reliability.
1. Enhanced Materials: Researchers have developed new materials that can withstand the intense radiation found in space. These materials are used in the construction of servers, providing increased durability and resistance to radiation.
2. Advanced Design: The design of radiation-hardened servers has been optimized to minimize the impact of radiation on hardware components. This includes incorporating shielding materials and using components that are less susceptible to radiation damage.
3. Redundancy: To ensure continuous operation, these servers are equipped with redundant systems. In the event of a component failure due to radiation exposure, the redundant system takes over, maintaining uninterrupted service.
4. Software Optimization: Software algorithms have been developed to detect and correct radiation-induced errors in real-time. This helps in maintaining data integrity and ensuring seamless operation.
Challenges in Achieving Full Reliability
Despite the advancements in radiation-hardened server technology, several challenges remain in achieving full reliability by 2028:
1. Radiation Levels: The level of radiation in space varies depending on the orbit and the time of year. Ensuring that servers can consistently withstand these varying levels of radiation remains a challenge.
2. Component Lifespan: The lifespan of radiation-hardened components is limited. Regular maintenance and replacement of these components are necessary to maintain server reliability.
3. Cost: The development and deployment of radiation-hardened servers are expensive. Finding cost-effective solutions while maintaining high reliability is a significant challenge.
4. Testing and Validation: Validating the reliability of radiation-hardened servers in a space environment requires extensive testing. Achieving accurate and comprehensive testing methods remains a challenge.
Conclusion
As we move closer to 2028, the importance of space-based data centers and the reliability of radiation-hardened servers cannot be overstated. While significant advancements have been made in this field, challenges remain in achieving full reliability. Continuous research, development, and innovation in radiation-hardened server technology are crucial to ensuring the success of space-based data centers and their role in driving technological advancements in the years to come.