In the wake of increasing global temperatures and the urgent need to mitigate climate change, the concept of climate reparations has gained significant traction. Climate reparations refer to the compensation paid to developing nations for the historical and ongoing contributions to climate change by developed countries. This article explores the innovative use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in optimizing carbon credit distribution models for climate reparations.
The Importance of Carbon Credits

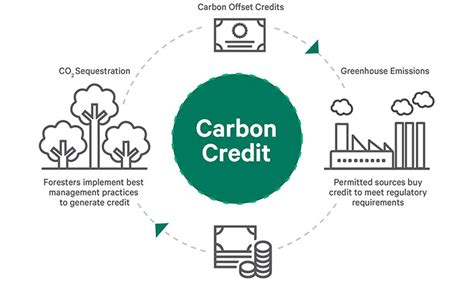
Carbon credits are a vital tool in the fight against climate change, as they provide a financial incentive for businesses and individuals to reduce their carbon emissions. These credits can be generated through various projects that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, such as renewable energy installations, forest conservation, and energy efficiency improvements.
The distribution of carbon credits is a critical component of climate reparations, as it ensures that developing nations receive fair compensation for their contributions to climate change. However, the current carbon credit distribution models often suffer from several drawbacks, such as inefficiency, transparency issues, and unequal distribution.
AI-Optimized Carbon Credit Distribution Models
Artificial Intelligence can play a crucial role in addressing these challenges by optimizing carbon credit distribution models. Here are some ways in which AI can be leveraged:
1. Data Analysis and Prediction: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, including historical emission records, climate patterns, and project performance, to predict the most effective carbon credit distribution strategies. This can help ensure that funds are allocated to the most impactful projects and nations.
2. Enhanced Transparency: AI can facilitate greater transparency in the carbon credit market by monitoring and auditing the distribution process. This can help prevent fraud and ensure that funds are used as intended.
3. Dynamic Allocation: AI can enable dynamic allocation of carbon credits based on real-time data, such as changing emission levels and project progress. This can help ensure that the distribution model remains adaptable and effective over time.
4. Equity and Inclusion: AI algorithms can help identify underserved communities and regions, ensuring that carbon credit distribution is equitable and inclusive. This can help bridge the gap between developed and developing nations in the fight against climate change.
5. Project Selection and Evaluation: AI can assist in selecting and evaluating carbon credit projects based on their potential for reducing emissions and promoting sustainable development. This can help ensure that funds are invested in the most effective and socially responsible projects.
Challenges and Considerations
While AI-optimized carbon credit distribution models offer promising solutions, several challenges and considerations must be addressed:
1. Data Privacy: Ensuring the privacy and security of sensitive data is crucial in an AI-driven carbon credit distribution system.
2. Bias and Fairness: AI algorithms can inadvertently perpetuate biases, so it is essential to design and implement models that promote fairness and equity.
3. Regulatory Compliance: AI-optimized carbon credit distribution models must comply with existing regulations and be adaptable to future changes in policy and technology.
4. Stakeholder Collaboration: Successful implementation of AI-optimized carbon credit distribution models requires collaboration between governments, businesses, and civil society organizations.
In conclusion, AI-optimized carbon credit distribution models have the potential to revolutionize the way climate reparations are administered. By harnessing the power of AI, we can ensure that carbon credits are distributed fairly, effectively, and transparently, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable and equitable future for all.