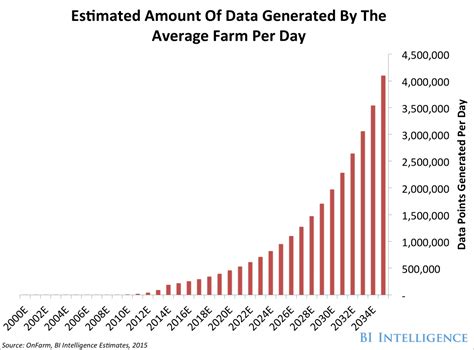
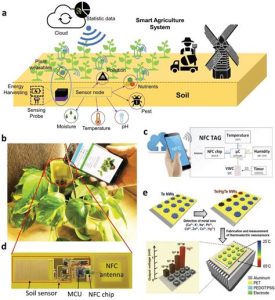
In the rapidly evolving landscape of agriculture, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a pivotal factor in shaping the future of crop yield. By 2030, the distinction between autonomous farming AI and traditional crop yield practices is expected to be more pronounced than ever. This article delves into a comparative analysis of these two methodologies, highlighting the potential yield outcomes by the turn of the decade.
### Introduction

Agriculture, as an industry, has historically relied on traditional farming practices that have been refined over centuries. However, with the advent of AI and automation, a new era of farming is emerging. Autonomous farming AI involves the use of sophisticated technologies such as drones, sensors, and machine learning algorithms to optimize crop production. This article aims to compare the yield potential of autonomous farming AI with traditional crop yield practices by 2030.
### Autonomous Farming AI: The Future of Agriculture
#### Drones and Sensors
Autonomous farming AI leverages drones equipped with advanced sensors to monitor crop health, soil conditions, and water levels. These drones can cover vast areas in a short period, providing real-time data that enables farmers to make informed decisions. The precision in applying fertilizers, pesticides, and water is significantly improved, leading to more efficient use of resources.
#### Machine Learning and Predictive Analytics
Machine learning algorithms analyze historical data and current conditions to predict potential crop yields. By anticipating weather patterns, pest outbreaks, and other factors, farmers can take preemptive measures to safeguard their crops. This predictive capability is crucial for ensuring high yields in the face of unpredictable environmental conditions.
#### Automation and Efficiency
Automated systems can perform tasks such as planting, harvesting, and even weeding. By reducing the need for manual labor, autonomous farming AI can increase efficiency and reduce costs. This efficiency translates into higher yields, as more resources are allocated to the actual growth of the crops.
### Traditional Crop Yield Practices
#### Soil Management
Traditional farming practices emphasize soil health and fertility. Farmers use organic matter, crop rotation, and other techniques to maintain soil quality, which is crucial for sustainable crop yield. However, these practices can be labor-intensive and time-consuming.
#### Water Management
Water is a critical resource in agriculture. Traditional farming methods often rely on flood irrigation or surface water, which can be inefficient and lead to water wastage. Modern methods like drip irrigation have improved water usage, but traditional practices still play a significant role in crop yield.
#### Crop Diversity
Diversifying crops can help mitigate the risk of crop failure due to pests, diseases, or adverse weather conditions. Traditional farming practices often promote crop diversity, but the extent of this diversity varies widely.
### Comparison by 2030
By 2030, it is expected that autonomous farming AI will have a significant impact on crop yield. The integration of AI and automation is likely to result in the following outcomes:
– **Increased Yields**: Autonomous farming AI is expected to yield higher crop yields compared to traditional practices, primarily due to improved resource management and predictive analytics.
– **Sustainability**: AI-driven farming methods are likely to be more sustainable, as they optimize the use of resources and reduce waste.
– **Cost Efficiency**: While the initial investment in AI technology may be high, the long-term cost savings from increased yields and reduced labor requirements could make it a cost-effective solution.
### Conclusion
The comparison between autonomous farming AI and traditional crop yield practices by 2030 reveals a clear trend towards the adoption of AI-driven solutions. While traditional methods will continue to play a role in agriculture, the integration of AI is poised to revolutionize the industry. By focusing on efficiency, sustainability, and predictive analytics, autonomous farming AI is set to become the cornerstone of high-yield crop production in the coming years.