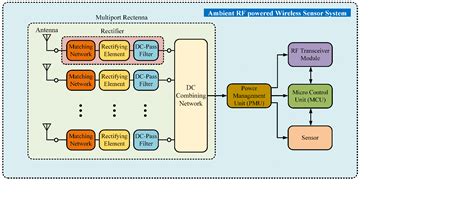
In the rapidly evolving landscape of the Internet of Things (IoT), one of the most significant challenges remains the power source for sensors. Traditional batteries have limitations in terms of lifespan and environmental impact. This is where zero-power IoT sensors, powered by radio frequency (RF) energy harvesting, come into play. By 2028, we have witnessed remarkable breakthroughs in the efficiency of RF energy harvesting, transforming the future of IoT technology.
The Promise of Zero-Power IoT Sensors

Zero-power IoT sensors represent a paradigm shift in the field of wireless sensor networks. These sensors are designed to operate without external power sources, drawing energy directly from ambient radio waves. This innovative technology has the potential to revolutionize various industries, including healthcare, smart cities, and industrial automation.
RF Energy Harvesting Efficiency Breakthroughs
1. Advanced Antenna Design
One of the key factors in RF energy harvesting is the antenna design. By 2028, significant advancements have been made in the design of antennas, enabling higher efficiency and wider frequency range. These antennas are capable of capturing a broader spectrum of radio waves, maximizing energy conversion.
2. Improved Power Conversion Technology
The efficiency of RF energy harvesting depends heavily on the power conversion technology. In the past few years, researchers have developed novel power conversion circuits that can efficiently convert the harvested RF energy into usable electrical power. These circuits are now more compact, reliable, and energy-efficient, making them ideal for zero-power IoT sensors.
3. Advanced Materials
The use of advanced materials in RF energy harvesting has been a game-changer. Graphene, for instance, has shown remarkable properties in terms of conductivity and flexibility, making it an excellent candidate for energy harvesting applications. By 2028, the integration of these materials into energy harvesting systems has resulted in higher efficiency and lower power consumption.
4. Smart Algorithms
The efficiency of RF energy harvesting can be further enhanced through the use of smart algorithms. These algorithms optimize the energy harvesting process by dynamically adjusting the sensor’s operating parameters based on the available energy. By 2028, sophisticated algorithms have been developed that can significantly improve the overall efficiency of zero-power IoT sensors.
Real-World Applications
The breakthroughs in RF energy harvesting efficiency have paved the way for numerous real-world applications of zero-power IoT sensors:
1. Wearable Devices: In the healthcare industry, zero-power IoT sensors can be integrated into wearable devices to monitor vital signs and health conditions without the need for battery replacement.
2. Smart Cities: Zero-power sensors can be deployed in smart cities to monitor environmental conditions, traffic patterns, and public safety, contributing to a more sustainable and efficient urban environment.
3. Industrial Automation: In industrial settings, zero-power sensors can be used to monitor equipment performance, predictive maintenance, and process optimization, leading to increased productivity and cost savings.
4. Agriculture: Zero-power IoT sensors can be employed in precision agriculture to monitor soil moisture, temperature, and other environmental factors, enabling farmers to make informed decisions and optimize crop yields.
Conclusion
The breakthroughs in RF energy harvesting efficiency have brought us closer to a future where zero-power IoT sensors become a reality. By 2028, these sensors have the potential to transform various industries, making them more sustainable, efficient, and reliable. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative applications of zero-power IoT sensors, shaping the next generation of the Internet of Things.