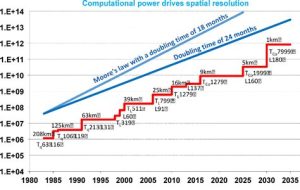
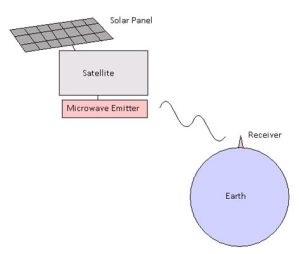
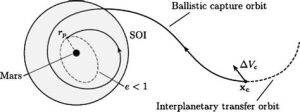
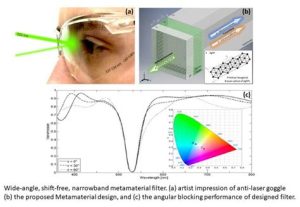
Introduction:
The advancement of renewable energy sources is crucial for combating climate change and reducing our reliance on fossil fuels. One of the most promising technologies in this domain is the bionic leaf, which has the potential to convert solar energy into usable fuel. This article explores the solar-to-fuel conversion efficiency goals set for the bionic leaf technology by 2025.

1. Background of Bionic Leaf Technology:
The bionic leaf is a bio-inspired device that mimics the natural process of photosynthesis. It consists of a leaf-like structure coated with catalysts that split water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen, and then convert the hydrogen into fuel. This technology offers a sustainable solution for producing clean, renewable energy.
2. Current State of Bionic Leaf Technology:
As of now, the efficiency of bionic leaf technology is relatively low, with some prototypes achieving around 1% efficiency. However, significant progress has been made in improving the device’s performance, and researchers are optimistic about achieving higher conversion rates by 2025.
3. Efficiency Goals for 2025:
By 2025, the efficiency goals for bionic leaf technology are set to reach around 10-15%. This would represent a substantial improvement over the current levels and bring the technology closer to commercial viability.
4. Factors Contributing to Improved Efficiency:
Several factors are expected to contribute to the increased efficiency of bionic leaf technology by 2025:
a. Enhanced Catalysts: Researchers are working on developing new catalysts that can more effectively split water molecules and convert hydrogen into fuel. This includes exploring materials such as perovskites, which have shown promising results in terms of stability and efficiency.
b. Improved Device Design: Optimizing the design of the bionic leaf, including the arrangement of catalysts and the overall structure, can enhance its efficiency. This may involve using 3D printing techniques to create customized devices that optimize the interaction between the catalysts and sunlight.
c. Enhanced Water Supply: Ensuring a steady supply of water to the bionic leaf is crucial for maintaining its efficiency. Researchers are exploring methods to optimize the water supply, such as integrating the device with a water recirculation system or using a desalination process.
d. Increased Solar Absorption: Improving the device’s ability to absorb sunlight can increase its overall efficiency. This can be achieved by using materials with higher light-absorption properties or by incorporating multiple layers of catalysts to capture a wider range of the solar spectrum.
5. Potential Applications:
Achieving the 2025 efficiency goals for bionic leaf technology would open up numerous applications, including:
a. Off-grid Energy Generation: Bionic leaf technology can be used to generate fuel in remote areas where traditional energy sources are scarce or non-existent.
b. Mobile Power: The compact size and lightweight nature of the bionic leaf make it suitable for powering mobile devices, such as smartphones and laptops, during outdoor activities.
c. Greenhouse Gas Reduction: By producing fuel from renewable sources, the bionic leaf can contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.
Conclusion:
The bionic leaf technology holds great promise for converting solar energy into usable fuel. By setting efficiency goals for 2025, researchers are striving to make this technology more efficient and commercially viable. As advancements continue to be made, the bionic leaf could play a significant role in the transition towards a sustainable and renewable energy future.