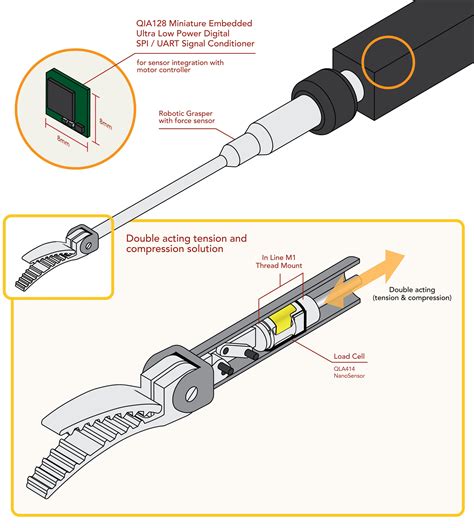
In the not-too-distant future, the landscape of medical procedures is poised to transform with the advent of robotic surgery. The year 2030 marks a significant milestone in the evolution of this technology, as advancements in haptic feedback and reduced latency thresholds pave the way for remote surgical interventions. This article explores the intersection of these innovations, their implications for healthcare, and the potential challenges they may pose.
### The Evolution of Robotic Surgery

Robotic surgery has been revolutionizing surgical practices for over two decades. The first robotic surgery system, the da Vinci Surgical System, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2000. Since then, robotic technology has been increasingly integrated into various surgical specialties, including urology, gynecology, and cardiothoracic surgery.
### Haptic Feedback: A New Dimension
Haptic feedback refers to the sense of touch provided to a user through a robotic system. This technology allows surgeons to feel the resistance and texture of tissues during a surgical procedure, similar to what they would experience during a conventional operation. The incorporation of haptic feedback has significantly improved the precision and control of robotic surgery, enabling surgeons to perform complex operations with increased dexterity.
### Latency Thresholds and Remote Operations
One of the most promising developments in robotic surgery is the reduction of haptic feedback latency. Latency refers to the time it takes for a signal to travel from the surgical instrument to the surgeon’s hands and back. In traditional robotic systems, latency can be a critical factor, potentially compromising the surgeon’s ability to perform delicate operations.
By 2030, advancements in technology are expected to bring the haptic feedback latency threshold down to a mere few milliseconds. This reduction will enable surgeons to conduct remote surgical interventions with the same level of precision and control as if they were operating in the same room as the patient.
### Benefits of Remote Operations
The combination of reduced latency and enhanced haptic feedback has numerous benefits for both patients and healthcare providers:
1. **Accessibility**: Patients in remote or underserved areas can access specialized surgical care from renowned surgeons across the globe.
2. **Specialization**: Surgeons can perform complex procedures that may not be available in their local hospitals, expanding their expertise and patient care options.
3. **Training**: Medical students and residents can benefit from real-time, hands-on training from experienced surgeons, enhancing their skills and knowledge.
### Challenges and Considerations
While the future of robotic surgery looks promising, there are several challenges that need to be addressed:
1. **Technology Costs**: High-tech robotic systems and maintenance can be expensive, potentially limiting access for some healthcare providers and patients.
2. **Regulatory Approval**: Ensuring that new technologies meet safety and efficacy standards will be crucial for widespread adoption.
3. **Ethical Concerns**: Ensuring patient privacy and consent, especially in remote operations, will be a significant concern.
### Conclusion
As we move towards 2030, robotic surgery with haptic feedback and reduced latency thresholds for remote operations is poised to transform the landscape of medical procedures. While challenges remain, the potential benefits for patients, healthcare providers, and the medical field at large are immense. By addressing these challenges and embracing innovation, we can look forward to a future where surgery is safer, more accessible, and tailored to individual patient needs.