# Meteorological Warfare Ethics 2040: Cloud Seeding for Drought Mitigation and the Laws in Place
In the year 2040, as the climate crisis intensifies, nations are turning to advanced technologies to combat the devastating effects of drought. Cloud seeding, a method of manipulating cloud formation to increase rainfall, has emerged as a crucial tool in the arsenal of meteorological warfare. However, with this technology comes a host of ethical considerations and legal challenges. This article delves into the ethical implications and the laws governing cloud seeding for drought mitigation in the coming decades.

## The Ethical Dilemma
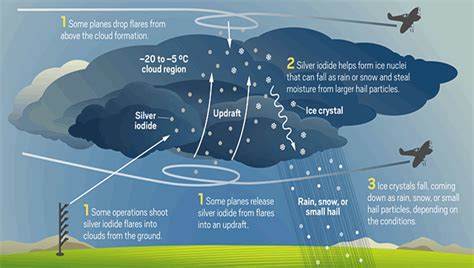
Cloud seeding has the potential to provide significant relief from droughts, ensuring water supplies for agriculture, drinking, and other essential needs. However, the process of manipulating the weather raises ethical questions regarding the right to interfere with natural systems and the potential consequences of such interventions.
### Unintended Consequences
One of the primary ethical concerns is the potential for unintended consequences. Cloud seeding may alter precipitation patterns, affecting neighboring regions and potentially exacerbating water scarcity in other areas. This raises the question of responsibility—should nations be held accountable for the unintended effects of their weather modification efforts?
### Equitable Distribution
Another ethical issue is the equitable distribution of the benefits derived from cloud seeding. There is a risk that wealthier nations or regions with stronger weather modification programs could gain a disproportionate share of the benefits, exacerbating global inequalities.
### Transparency and Accountability
Transparency and accountability are crucial in the realm of meteorological warfare. It is essential for nations to be open about their cloud seeding programs, sharing information on their activities, outcomes, and potential risks. This promotes trust and allows for international cooperation in addressing the global climate crisis.
## The Laws in Place
In response to the ethical and practical challenges of cloud seeding, several laws and regulations have been implemented to govern its use.
### International Treaties
Several international treaties, such as the Convention on the Prohibition of Military or Any Other Hostile Use of Environmental Modification Techniques, prohibit the use of weather modification for military purposes. While cloud seeding is not explicitly mentioned in this treaty, it serves as a foundation for the ethical and legal framework surrounding weather modification.
### National Regulations
Individual countries have implemented their own regulations to oversee cloud seeding programs. These regulations typically address issues such as environmental impact assessments, the use of chemicals for cloud seeding, and the sharing of information on weather modification activities.
### The United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD)
The UNCCD provides a framework for international cooperation in addressing desertification and drought. Under this convention, countries are encouraged to engage in drought mitigation efforts, including cloud seeding, while ensuring that such efforts are environmentally sound and socially equitable.
## Conclusion
As we approach 2040, cloud seeding for drought mitigation presents both opportunities and challenges. While the technology has the potential to provide significant relief from droughts, it also raises ethical and legal questions that must be addressed. By implementing international treaties, national regulations, and fostering transparency and accountability, we can navigate the complex landscape of meteorological warfare and work towards a more sustainable future.