Introduction:
The landscape of clinical trials is undergoing a significant transformation with the advent of decentralized trials and blockchain technology. These advancements offer a new approach to patient data ownership, ensuring privacy, security, and efficiency in the research process. This article explores the intersection of decentralized clinical trials, blockchain, and patient data ownership models.

Decentralized Clinical Trials:
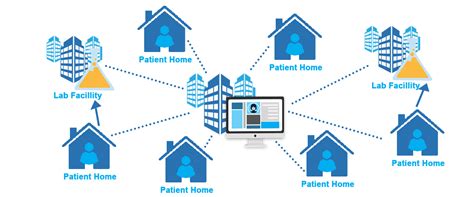
Decentralized clinical trials (DCTs) involve the use of digital platforms to conduct research remotely, allowing participants to engage in trials from various locations. This approach eliminates the need for centralized study sites, reduces travel costs, and increases the diversity of participants. DCTs leverage technology to streamline the trial process, from patient recruitment to data collection and analysis.
Blockchain Technology:
Blockchain, a decentralized and distributed ledger technology, provides a secure and transparent platform for storing and managing data. Its inherent features, such as immutability, encryption, and consensus mechanisms, make it an ideal solution for clinical trials. Blockchain can ensure the integrity of patient data, reduce fraud, and facilitate real-time data sharing among stakeholders.
Patient Data Ownership Models:
Patient data ownership models refer to the legal and ethical frameworks that govern how patient data is collected, stored, and used in clinical trials. These models aim to protect patient privacy, ensure informed consent, and promote transparency in data sharing. Blockchain technology can play a crucial role in implementing these models by providing a secure and transparent platform for patient data ownership.
1. Patient-Centric Ownership:
Patient-centric ownership models empower patients to have control over their data. Blockchain can enable patients to grant or revoke access to their data, ensuring they remain in control of their personal information. By utilizing smart contracts, patients can set specific conditions for data sharing, such as consent-based access or anonymization requirements.
2. Data Sharing Agreements:
Blockchain can facilitate the creation of secure and enforceable data sharing agreements between patients, researchers, and other stakeholders. These agreements can outline the terms and conditions of data sharing, including consent, usage limitations, and data anonymization. By using blockchain, parties can have a transparent and immutable record of their agreements, reducing the risk of disputes and ensuring compliance.
3. Data Anonymization and Privacy:
Blockchain technology can be used to anonymize patient data while preserving its integrity. By encrypting sensitive information and using cryptographic techniques, blockchain can ensure that patient data remains private and secure. This approach allows researchers to access and analyze anonymized data without compromising patient privacy.
4. Enhanced Transparency and Accountability:
Blockchain provides a transparent and immutable ledger of all transactions and data exchanges. This feature enhances accountability among stakeholders, as they can track the flow of data and verify its authenticity. By using blockchain, clinical trials can achieve greater transparency, fostering trust and confidence among patients and researchers.
Conclusion:
Decentralized clinical trials, powered by blockchain technology, offer a promising solution for patient data ownership. By implementing patient-centric ownership models, blockchain can ensure privacy, security, and transparency in the management of patient data. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, embracing these advancements will pave the way for more efficient, ethical, and patient-centered clinical trials.