Introduction:
The field of neuromorphic computing has been rapidly evolving, aiming to replicate the structure and function of the human brain in electronic systems. One of the key aspects of this evolution is the increase in synaptic density, which directly impacts the performance and efficiency of neuromorphic chips. This article compares the synaptic density benchmarks of neuromorphic chips in 2025 and 2030, highlighting the advancements made in this field.

2025 Synaptic Density Benchmarks:
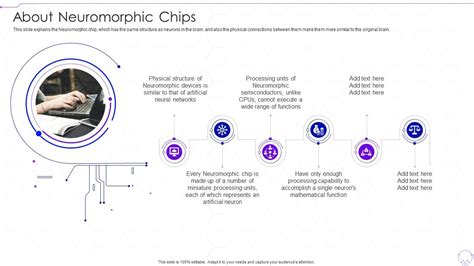
In 2025, neuromorphic chips have reached a significant milestone in terms of synaptic density. The benchmark for synaptic density in this year is estimated to be around 10^10 synapses per chip. This represents a substantial improvement over the previous generations, which had densities ranging from 10^7 to 10^9 synapses.
The increase in synaptic density can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, advancements in nanotechnology have enabled the development of smaller transistors and interconnects, which in turn allow for a higher number of synapses to be integrated on a single chip. Secondly, the use of memristive technology has facilitated the creation of non-volatile, analog synapses that can store information without the need for power. Lastly, the optimization of neuromorphic architectures has led to a more efficient utilization of resources, further enhancing synaptic density.
2025 Synaptic Density Applications:
The high synaptic density of neuromorphic chips in 2025 has paved the way for various applications. These include:
1. Artificial intelligence: The increased synaptic density allows for more complex neural networks to be implemented on a single chip, enabling more accurate and efficient AI algorithms.
2. Image recognition: With higher synaptic density, neuromorphic chips can process large-scale image recognition tasks with reduced computational requirements and power consumption.
3. Autonomous systems: The improved performance of neuromorphic chips in 2025 makes them suitable for real-time processing in autonomous vehicles and drones, enhancing safety and efficiency.
4. Brain-inspired computing: The high synaptic density enables the creation of brain-inspired computing systems that can simulate brain-like functions, such as memory and learning.
2030 Synaptic Density Benchmarks:
By 2030, the synaptic density of neuromorphic chips is expected to have significantly increased, reaching a benchmark of around 10^14 synapses per chip. This dramatic increase is driven by further advancements in nanotechnology, memristive technology, and neuromorphic architecture design.
2030 Synaptic Density Applications:
The higher synaptic density in 2030 will enable a wide range of applications, including:
1. Complex AI algorithms: The increased synaptic density allows for the implementation of even more complex neural networks, enabling advanced AI applications such as natural language processing and speech recognition.
2. High-resolution image processing: With higher synaptic density, neuromorphic chips can process high-resolution images with improved accuracy and reduced latency.
3. Real-time decision-making in autonomous systems: The enhanced performance of neuromorphic chips in 2030 will enable real-time decision-making in autonomous systems, such as advanced robotics and smart cities.
4. Neurological disorders: The high synaptic density allows for the development of brain-inspired computing systems that can be used to study and treat neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease and epilepsy.
Conclusion:
The evolution of neuromorphic chips in terms of synaptic density has been remarkable, with significant advancements expected to be achieved by 2030. The increased synaptic density will lead to more powerful and efficient neuromorphic chips, enabling a wide range of applications in artificial intelligence, image processing, autonomous systems, and neurological research. As the field continues to progress, the potential for neuromorphic computing to revolutionize various industries is immense.