Introduction:
In recent years, the field of electronics has witnessed remarkable advancements, with one of the most significant being the development of self-healing electronics. These innovative devices have the ability to repair themselves when damaged, thereby extending their lifespan and reducing the need for frequent maintenance. This article delves into the world of self-healing electronics, focusing on the success rates of microcapsule polymer circuit repairs.

Background:
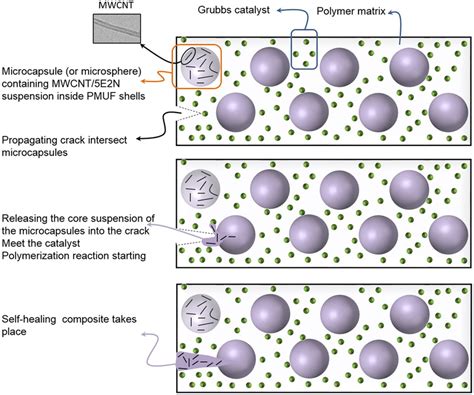
Self-healing electronics rely on the use of microcapsules containing a healing agent, which is released when the device is damaged. The healing agent then reacts with the damaged material, restoring its original properties. Microcapsule polymer circuits are a popular choice for self-healing applications due to their flexibility, durability, and ease of integration into various devices.
Types of Microcapsule Polymer Circuits:
There are several types of microcapsule polymer circuits, each with its unique advantages and applications. Some of the most common types include:
1. Conductive polymer circuits: These circuits use conductive polymers as the healing agent, enabling the repair of electrical connections.
2. Dielectric polymer circuits: These circuits utilize dielectric polymers to restore the insulation properties of the damaged material.
3. Piezoelectric polymer circuits: These circuits incorporate piezoelectric polymers, which generate an electric charge when subjected to mechanical stress, facilitating the healing process.
Success Rates of Microcapsule Polymer Circuit Repairs:
The success rates of microcapsule polymer circuit repairs depend on various factors, including the type of material, the extent of damage, and the healing process. Here are some key points to consider:
1. Material selection: The choice of polymer material plays a crucial role in the success rate of repairs. Some polymers may have better healing properties than others, making them more suitable for specific applications.
2. Damage severity: The success rate decreases as the severity of damage increases. Minor cracks or breaks may be easily repaired, while extensive damage may require more complex healing processes.
3. Healing process: The efficiency of the healing process is another important factor. Some healing agents may react more quickly and effectively than others, leading to higher success rates.
Recent advancements and future prospects:
Research in the field of self-healing electronics has led to significant improvements in microcapsule polymer circuit repair success rates. Some of the recent advancements include:
1. Enhanced healing agents: New healing agents have been developed that offer faster and more effective repair capabilities.
2. Improved encapsulation techniques: Advanced encapsulation methods have been employed to ensure that the healing agent is released only when needed.
3. Integration of sensors: The integration of sensors into self-healing electronics allows for real-time monitoring of the healing process, leading to better control and higher success rates.
Conclusion:
Self-healing electronics, particularly microcapsule polymer circuits, have the potential to revolutionize the field of electronics. With ongoing research and development, the success rates of microcapsule polymer circuit repairs are expected to continue improving, making these devices more reliable and durable. As technology advances, we can look forward to a future where self-healing electronics become a standard feature in various devices, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.