In the rapidly evolving field of quantum technology, one of the most intriguing advancements is the development of quantum radar. This innovative technology has the potential to revolutionize various sectors, including defense, communication, and environmental monitoring. However, the effectiveness of quantum radar is threatened by stealth techniques that can evade detection. This article delves into the fascinating world of quantum radar, entangled photon detection, and the evasion strategies employed by stealth technologies.
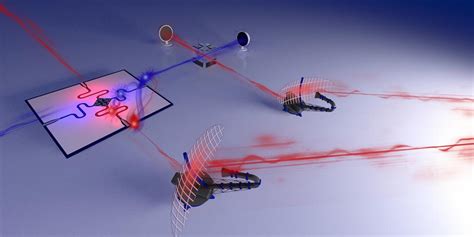
Quantum radar is a cutting-edge technology that utilizes the principles of quantum mechanics to detect and track objects. Unlike traditional radar systems, quantum radar can achieve superior performance by exploiting the properties of entangled photons. Entangled photons are particles that are correlated in such a way that the state of one photon is instantaneously connected to the state of the other, regardless of the distance between them. This unique property allows quantum radar to detect objects with unprecedented accuracy and sensitivity.

The detection of entangled photons is the cornerstone of quantum radar technology. When a quantum radar system emits entangled photons, these photons interact with the target object and scatter. The scattered photons then return to the radar, where they are measured and analyzed to determine the target’s position, velocity, and other characteristics. However, this process is not without its challenges.
One of the primary challenges faced by quantum radar is the development of effective evasion techniques. Stealth technologies are designed to counter radar detection by minimizing the target’s radar cross-section (RCS) and other detectable signatures. Here are some of the most prominent evasion techniques employed by stealth technologies:
1. Radar Cross-Section Reduction: Stealth technologies often employ various methods to reduce the RCS of a target. This includes shaping the target’s surface to minimize the reflection of radar waves, using radar-absorbent materials, and employing materials with a low dielectric constant.
2. Radar Absorption: Stealth technologies may use radar-absorbent materials to absorb the incoming radar waves, thereby reducing the amount of energy reflected back to the radar system.
3. Electronic Countermeasures (ECM): ECM techniques involve the use of electronic devices to interfere with or jam the radar signal, making it difficult for the radar system to detect the target.
4. Active Emission: Some stealth technologies use active emission techniques, where the target emits a signal that is difficult for the radar system to detect. This can be achieved by using a signal that is outside the radar’s frequency range or by using a signal that is masked by other signals.
5. Quantum Evasion: In the context of quantum radar, quantum evasion techniques involve the use of quantum cryptography and other quantum information processing methods to manipulate the entangled photons in such a way that they are difficult to detect and analyze.
To counter these evasion techniques, quantum radar developers are working on advanced detection algorithms and signal processing methods. These methods aim to identify and mitigate the effects of stealth technologies, ensuring that quantum radar remains an effective tool for various applications.
In conclusion, quantum radar holds immense potential for various applications, but it faces significant challenges from stealth technologies. By understanding and developing advanced evasion techniques, we can ensure that quantum radar remains a formidable tool in the future. As the field of quantum technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative solutions to the challenges posed by stealth technologies, paving the way for a new era of secure and effective radar systems.