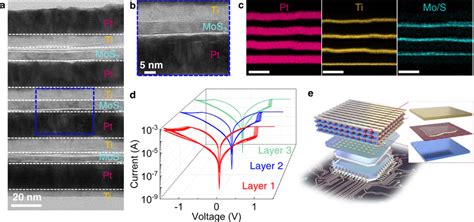
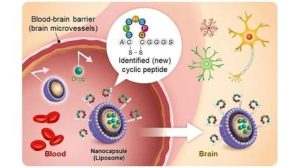
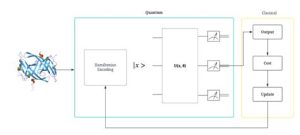
Introduction:
The advent of the Post-Moore’s Law era has brought about significant challenges in the semiconductor industry. As traditional scaling methods reach their limits, innovative technologies like 3D stacked memristor chips are being explored to maintain the pace of innovation. However, managing the thermal challenges associated with these advanced chips is a critical concern. This article delves into the thermal management challenges faced in the Post-Moore’s Law era, focusing on 3D stacked memristor chips.

1. The Need for 3D Stacked Memristor Chips:
As transistors continue to shrink, heat dissipation becomes increasingly difficult. This has led to the development of 3D stacked memristor chips, which offer several advantages over traditional 2D planar technologies. These benefits include higher density, improved performance, and reduced power consumption. However, the increased complexity of 3D stacked memristor chips also brings about significant thermal management challenges.
2. Thermal Challenges in 3D Stacked Memristor Chips:
a. High Power Density: 3D stacked memristor chips pack a large number of transistors in a compact space, leading to high power density. This high power density generates a significant amount of heat, making thermal management a crucial issue.
b. Heat Conduction Pathways: The 3D stacking of memristor chips introduces complex heat conduction pathways. Ensuring efficient heat dissipation throughout the chip becomes challenging due to the intricate interconnects and vias.
c. Heat Spreading: The heat generated by the active components in the chip needs to be spread out effectively to prevent hotspots. Achieving uniform heat distribution in a 3D stacked memristor chip is a complex task.
3. Thermal Management Strategies:
a. Heat Sinks: Integrating heat sinks into the chip design can help dissipate heat effectively. These heat sinks can be in the form of metal layers or vias that provide a larger surface area for heat dissipation.
b. Thermal vias: Designing thermal vias with a larger diameter and better thermal conductivity can enhance heat conduction from the chip to the external heat sink.
c. Heat Spreader Layers: Adding heat spreader layers between the chip and the heat sink can help in dissipating heat uniformly across the chip surface.
d. Advanced Packaging Techniques: Utilizing advanced packaging techniques, such as fan-out wafer-level packaging, can improve thermal performance by providing better heat dissipation pathways.
e. Intelligent Thermal Control: Implementing intelligent thermal control algorithms can help monitor and manage the temperature of the chip in real-time, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Conclusion:
The Post-Moore’s Law era has brought about new challenges in thermal management for 3D stacked memristor chips. Addressing these challenges requires innovative approaches and strategies. By implementing advanced packaging techniques, intelligent thermal control algorithms, and efficient heat dissipation methods, the semiconductor industry can continue to push the boundaries of innovation while ensuring the reliability and performance of these advanced chips.