Introduction:
Space-based solar power (SBSP) has emerged as a promising solution to address the global energy crisis and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. One of the key challenges in harnessing space-based solar power is the efficient transmission of energy from space to Earth. This article explores the microwave transmission efficiency loss models associated with space-based solar power, providing insights into the technical and logistical aspects of this innovative energy technology.

I. Overview of Space-Based Solar Power
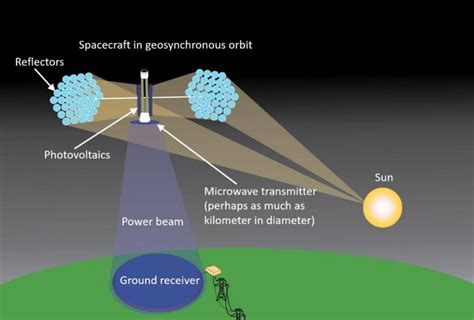
Space-based solar power involves the use of large solar arrays placed in geostationary orbit around Earth. These arrays capture solar energy, convert it into electricity, and then transmit the power back to Earth using microwaves or laser beams. This technology offers several advantages, including constant access to solar energy and the potential to generate electricity on a global scale.
II. Microwave Transmission
Microwave transmission is a preferred method for space-based solar power due to its high efficiency and relatively low atmospheric losses. However, the efficiency of this transmission process can be affected by various factors, such as signal attenuation, beam divergence, and interference.
III. Efficiency Loss Models
A. Signal Attenuation
Signal attenuation refers to the reduction in signal power as it travels through the atmosphere and space. The primary factors contributing to signal attenuation are atmospheric gases, clouds, and rain. The attenuation can be modeled using empirical formulas and atmospheric models, such as the International Telecommunication Union’s (ITU) attenuation model.
B. Beam Divergence
Beam divergence is another critical factor that affects the efficiency of microwave transmission. The beam divergence angle depends on the aperture size of the transmitting and receiving antennas, as well as the distance between them. A larger divergence angle leads to a wider beam, which can result in increased power loss and reduced transmission efficiency. Beam divergence can be modeled using geometric optics and antenna pattern analysis.
C. Interference
Interference from other microwave signals can significantly impact the efficiency of space-based solar power transmission. Interference can be caused by terrestrial communication systems, satellite signals, and cosmic noise. To model interference, one can analyze the frequency spectrum and identify potential sources of interference. Techniques such as frequency hopping and interference cancellation can be employed to mitigate interference effects.
IV. Simulation and Optimization
To optimize the efficiency of space-based solar power microwave transmission, it is essential to simulate the transmission process and evaluate the performance of various antenna designs and transmission configurations. Simulation tools, such as electromagnetic simulation software and high-frequency structure simulator (HFSS), can be used to model the microwave transmission process and predict the efficiency losses.
V. Conclusion
Space-based solar power offers a promising solution to meet the world’s growing energy demand. However, the efficient transmission of energy from space to Earth remains a critical challenge. This article has explored the microwave transmission efficiency loss models associated with space-based solar power, highlighting the importance of considering factors such as signal attenuation, beam divergence, and interference. By understanding and mitigating these factors, we can enhance the efficiency and feasibility of space-based solar power transmission, paving the way for a sustainable and abundant energy future.