In the ever-evolving field of medical technology, 4D printing has emerged as a revolutionary technique for creating advanced biomaterials with shape-memory properties. This innovative approach is transforming the deployment of medical implants, offering unprecedented precision and customization. This article explores the fascinating world of 4D printing biomaterials and their potential to revolutionize the medical implant industry.
Understanding 4D Printing

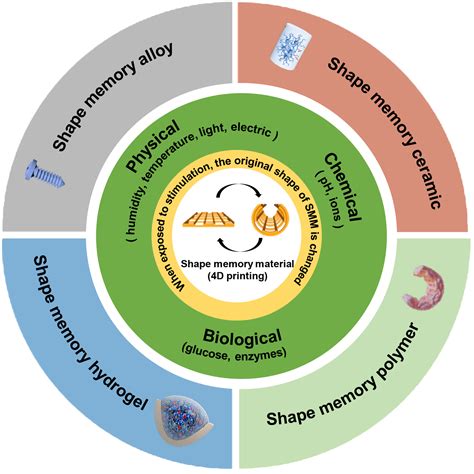
4D printing is an extension of traditional 3D printing, where the printed objects can change shape over time, temperature, or external stimuli. This unique ability to transform allows for a wide range of applications in various fields, including medicine. In the context of medical implants, 4D printing biomaterials enable the creation of implants that can adapt to the body’s environment and requirements, providing enhanced functionality and comfort for patients.
Shape-Memory Medical Implants
Shape-memory materials have been used in medical applications for many years, particularly in orthopedics and cardiovascular surgery. These materials can return to their original shape after being deformed, which is highly beneficial for medical implants. However, traditional shape-memory materials often lack the ability to be customized or modified for specific patient needs.
4D printing biomaterials address this limitation by combining the properties of shape-memory materials with the advantages of 3D printing technology. By incorporating a variety of biomaterials, such as hydrogels, polymers, and metals, researchers can create implants with tailored properties that can adapt to the patient’s anatomy and requirements.
The Deployment Process
The deployment of 4D printing biomaterials for medical implantation involves several steps:
1. Design: Medical professionals work with engineers and designers to create a 3D model of the implant that incorporates the desired shape-memory properties and biomaterials.
2. 4D Printing: The 3D model is then converted into a 4D printed biomaterial using a specialized 4D printer that can control the shape and properties of the material.
3. Implantation: The 4D printed biomaterial is inserted into the patient’s body, where it will gradually transform to its final shape and function.
4. Adaptation: Over time, the implant adapts to the patient’s anatomy, providing a comfortable and functional solution that can be easily adjusted if needed.
Advantages of 4D Printing Biomaterials
The use of 4D printing biomaterials for medical implant deployment offers several advantages:
1. Customization: Implants can be tailored to fit individual patient needs, increasing the chances of successful treatment and patient satisfaction.
2. Biocompatibility: 4D printing allows for the use of biocompatible materials, reducing the risk of rejection or complications.
3. Precision: The ability to control the shape and properties of the implant ensures precise and targeted treatment.
4. Adaptability: The shape-memory properties of 4D printed biomaterials enable the implant to adapt to the patient’s body, providing long-term stability and functionality.
The Future of 4D Printing in Medicine
The potential of 4D printing biomaterials for medical implant deployment is vast. As research and development continue, we can expect to see even more innovative applications in various medical fields, including:
1. Orthopedics: Customized, shape-memory implants for joints, bones, and tendons.
2. Cardiovascular surgery: Implants for heart valves, stents, and vascular grafts.
3. Neurology: Implants for treating neurological disorders and injuries.
4. Tissue engineering: 4D printed biomaterials for growing and regenerating damaged tissues.
In conclusion, 4D printing biomaterials for shape-memory medical implant deployment represent a groundbreaking advancement in the field of medical technology. This innovative approach has the potential to revolutionize the treatment of various medical conditions, offering customized, biocompatible, and adaptable solutions for patients worldwide.