In the year 2028, the world has witnessed a monumental shift in the way we perceive and protect the data derived from our brains. The Neuro Rights Movement, which gained momentum in the early 2020s, has now culminated in the establishment of Global Brain Data Protection Standards. This article delves into the background, objectives, and implications of these groundbreaking standards.
**Background**

The Neuro Rights Movement originated from the growing concern over the ethical implications of using brain data for various purposes, such as medical research, marketing, and surveillance. As technology advanced, the ability to read, interpret, and manipulate brain data became more sophisticated, raising questions about privacy, consent, and the potential for misuse.
The movement gained traction as individuals, advocacy groups, and policymakers alike recognized the need for a comprehensive framework to govern the use of brain data. This led to the formation of the Global Brain Data Protection Council (GBDPC), an international body tasked with developing and implementing the new standards.
**Objectives of Global Brain Data Protection Standards**
The primary objectives of the Global Brain Data Protection Standards are as follows:
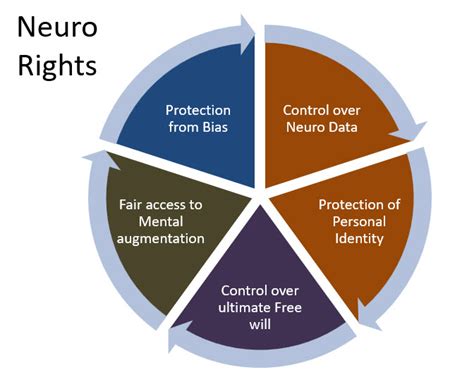
1. **Privacy Protection**: Ensuring that individuals have control over their brain data and the ability to consent to its use.
2. **Transparency**: Requiring organizations to disclose how they collect, store, and use brain data.
3. **Security**: Implementing robust measures to safeguard brain data from unauthorized access and breaches.
4. **Equity**: Ensuring that the benefits of brain data are shared fairly and do not exacerbate existing inequalities.
5. **Accountability**: Establishing clear guidelines for organizations to follow and mechanisms for enforcing compliance.
**Key Aspects of the Standards**
The Global Brain Data Protection Standards encompass several key aspects:
1. **Consent Mechanisms**: Individuals must provide explicit consent for the collection, storage, and use of their brain data. This includes the right to withdraw consent at any time.
2. **Data Minimization**: Organizations are required to collect only the data necessary for their intended purpose and to delete data that is no longer needed.
3. **Data Security**: Stringent encryption and access controls must be implemented to protect brain data from unauthorized access.
4. **Data Sharing**: Organizations must obtain explicit consent from individuals before sharing their brain data with third parties.
5. **Transparency**: Organizations must disclose how they collect, store, and use brain data, as well as the potential risks associated with such use.
**Implications**
The implementation of Global Brain Data Protection Standards has several implications:
1. **Ethical Considerations**: The standards promote ethical practices in the use of brain data, ensuring that individuals’ rights and well-being are prioritized.
2. **Technological Advancements**: The standards may accelerate the development of new technologies and applications for brain data, as organizations are more likely to invest in ethical and responsible practices.
3. **Global Collaboration**: The standards foster international cooperation in the regulation of brain data, ensuring that the benefits of brain data are shared equitably across borders.
4. **Economic Impact**: The standards may lead to the growth of a new industry focused on ethical brain data management, creating job opportunities and economic benefits.
In conclusion, the Neuro Rights Movement 2028 and the establishment of Global Brain Data Protection Standards mark a significant milestone in the protection of brain data. By prioritizing privacy, transparency, and security, these standards pave the way for a more ethical and responsible future in the use of brain data.