In the rapidly evolving field of renewable energy, artificial photosynthesis has emerged as a beacon of hope for the future. By mimicking the natural process of photosynthesis in plants, researchers have been able to convert solar energy into usable forms of energy, such as hydrogen. This groundbreaking technology promises to revolutionize the way we produce energy, reduce our carbon footprint, and create a more sustainable world. This article will delve into the current state of artificial photosynthesis, with a focus on the solar-to-hydrogen conversion benchmarks expected by 2025.
## The Concept of Artificial Photosynthesis

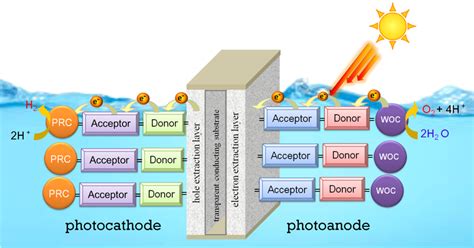
Artificial photosynthesis is a process that utilizes sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and hydrogen. This process is similar to the one carried out by plants during photosynthesis, except that it is designed to occur in an artificial setting. The main objective of this technology is to harness the immense power of the sun and convert it into a form of energy that can be stored and used as needed.
## Solar-to-Hydrogen Conversion
The heart of artificial photosynthesis lies in the solar-to-hydrogen conversion process. This involves splitting water molecules (H2O) into oxygen (O2) and hydrogen (H2) using sunlight as the energy source. The hydrogen produced can then be stored and used as a clean, renewable fuel for various applications, including transportation and power generation.
## Current State of Solar-to-Hydrogen Conversion
As of 2023, the solar-to-hydrogen conversion process has made significant progress. Researchers have developed various catalysts, materials, and devices that can efficiently carry out this conversion. However, there are still several challenges to be addressed before achieving widespread adoption of this technology.
### Catalysts
One of the key components in the solar-to-hydrogen conversion process is the catalyst, which facilitates the splitting of water molecules. Current research is focused on finding cheaper, more abundant, and more efficient catalysts. In recent years, perovskite and carbon-based catalysts have shown promising results, with some achieving energy conversion efficiencies of over 10%.
### Devices
The solar-to-hydrogen conversion process requires specialized devices known as photoelectrochemical cells. These cells consist of a semiconductor material, a catalyst, and an electrolyte. As of 2023, the efficiency of these cells has improved significantly, with some achieving record-breaking conversion efficiencies. However, the stability and cost of these devices remain challenges to be overcome.
## Benchmarks for 2025
Looking ahead to 2025, researchers have set several benchmarks for the solar-to-hydrogen conversion process. These benchmarks include:
### 1. Energy Conversion Efficiency
Efforts are being made to increase the energy conversion efficiency of solar-to-hydrogen conversion systems. By 2025, researchers aim to achieve an efficiency of at least 15%, which would be a significant improvement over current levels.
### 2. Catalyst Stability
Catalyst stability is crucial for the long-term viability of solar-to-hydrogen conversion systems. By 2025, researchers hope to develop catalysts that maintain their efficiency and activity for at least 5,000 hours without degradation.
### 3. Cost Reduction
The cost of producing solar-to-hydrogen conversion systems is another critical factor. By 2025, researchers aim to reduce the cost of these systems by at least 50%, making them more competitive with traditional energy sources.
## Conclusion
Artificial photosynthesis and solar-to-hydrogen conversion have the potential to revolutionize the renewable energy landscape. With ongoing research and development, we can expect significant advancements in this field by 2025. As these benchmarks are achieved, the world will be one step closer to a sustainable, carbon-neutral future.