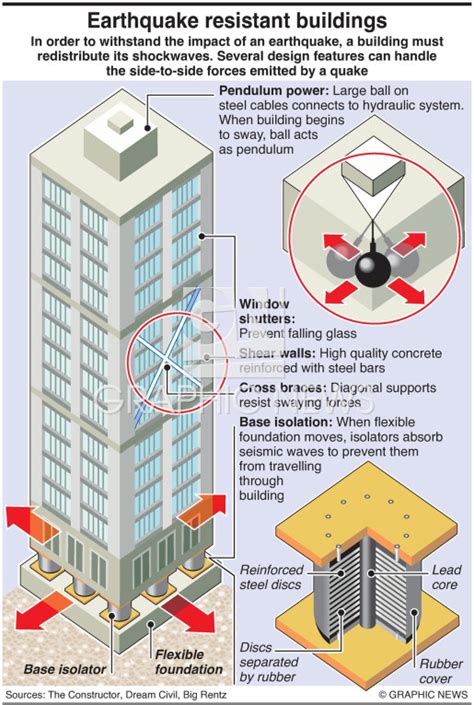
In the ever-evolving landscape of construction and urban development, the quest for disaster-resilient infrastructure has become more critical than ever. As we approach 2035, the urgency to build earthquake-proof structures grows, given the frequency and intensity of seismic activities around the world. This article explores the cutting-edge building materials that promise to make our future infrastructure more resilient to earthquakes.
**Introduction**

Earthquakes are a natural phenomenon that can cause catastrophic damage to buildings and infrastructure. The aftermath of such disasters can be devastating, leading to loss of life, property, and economic stability. As the global population continues to urbanize, the demand for robust and resilient structures is at an all-time high. The development of earthquake-proof building materials is a step towards creating a safer and more sustainable built environment.
**Advanced Concrete**
One of the most promising building materials for earthquake-resistant structures is advanced concrete. This material is known for its high compressive strength and durability. By incorporating fibers such as steel, glass, or polypropylene, the concrete can withstand tensile forces that typically lead to cracking and failure during seismic events.
**Geosynthetic Materials**
Geosynthetic materials, including geomembranes, geotextiles, and geogrids, are being increasingly used in earthquake-resistant construction. These materials are designed to distribute loads more evenly, reducing the risk of structural failure. Geosynthetic reinforcement can be integrated into foundations, retaining walls, and other critical components to enhance their performance during earthquakes.
**Smart Concrete**
Smart concrete is a revolutionary material that can sense and respond to changes in its environment. This material is embedded with sensors that detect stress levels, cracks, and other signs of damage. By providing real-time data, smart concrete enables engineers to take proactive measures, such as reinforcing vulnerable areas or triggering early warning systems, to mitigate the impact of seismic events.
**Modular Construction**
Modular construction involves the assembly of prefabricated building components in a controlled environment. This approach not only improves construction efficiency but also allows for the creation of earthquake-resistant structures. Modular buildings can be designed with flexible connections that allow them to move and bend during seismic activity, reducing the risk of collapse.
**Steel Structures**
Steel is a versatile material that has been used in earthquake-resistant construction for decades. Its high tensile strength and ductility make it an excellent choice for seismic-resistant designs. Steel structures can be designed to dissipate energy during earthquakes, minimizing the risk of catastrophic failure.
**Conclusion**
As we move towards 2035, the development of earthquake-proof building materials is crucial for creating a more resilient and sustainable infrastructure. By incorporating advanced concrete, geosynthetic materials, smart concrete, modular construction, and steel structures, we can build a future where the impact of earthquakes is minimized, and communities are better protected. The challenges ahead are significant, but with continued innovation and collaboration, we can pave the way for a safer and more secure world.