In the ever-evolving landscape of urban planning, technology has become an indispensable tool for cities seeking to manage their growth and development. One of the most pressing challenges faced by urban planners is the prediction and prevention of slum formation. This article delves into the contrasting approaches of AI-driven slum prediction algorithms and community input models, examining their strengths, limitations, and potential synergies.
AI-driven Slum Prediction Algorithms

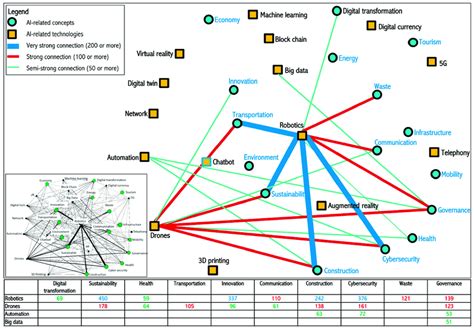
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized the field of urban planning by offering predictive analytics that can help identify potential slum formation areas. These algorithms analyze a multitude of data points, including demographic, economic, and environmental factors, to forecast the likelihood of slum development.
Strengths:
1. Efficiency: AI algorithms can process vast amounts of data at a rapid pace, enabling urban planners to identify high-risk areas quickly.
2. Objectivity: By eliminating human biases, AI-driven models can provide unbiased predictions.
3. Scalability: These algorithms can be easily adapted to different cities and regions, making them a versatile tool for urban planners.
Limitations:
1. Data Availability: The accuracy of AI-driven models heavily relies on the availability and quality of data. In many developing cities, data may be scarce or incomplete.
2. Over-reliance on Data: AI algorithms may overlook critical local factors that influence slum formation, leading to inaccurate predictions.
3. Lack of Contextual Understanding: AI-driven models often lack the nuanced understanding of local contexts, which is crucial for effective urban planning.
Community Input Models
On the other hand, community input models emphasize the importance of involving local residents in the urban planning process. These models collect data and insights from the community to inform the development of slum prevention strategies.
Strengths:
1. Inclusivity: By engaging local residents, these models ensure that diverse perspectives are considered in the planning process.
2. Contextual Understanding: Community input models provide valuable insights into the local context, enabling planners to address the specific needs and challenges of the area.
3. Empowerment: Involving the community in the planning process can empower residents and foster a sense of ownership over their living environment.
Limitations:
1. Time-consuming: Collecting and analyzing community input can be a lengthy process, which may delay the implementation of slum prevention strategies.
2. Subjectivity: Community input can be influenced by various factors, including social, economic, and political contexts, which may introduce subjectivity into the planning process.
3. Resource Intensive: Community engagement requires dedicated resources, including personnel and funding, which may not be readily available in all cities.
Synergies between AI and Community Input Models
While AI-driven slum prediction algorithms and community input models present distinct approaches, there is potential for synergy between the two. By combining the efficiency and objectivity of AI with the inclusivity and contextual understanding of community input, urban planners can create more effective slum prevention strategies.
1. Data Integration: Urban planners can use AI algorithms to process large datasets, while simultaneously incorporating community input to refine the predictions and identify specific risk factors.
2. Collaborative Decision-Making: By involving both AI-driven models and community input, planners can make more informed decisions that reflect the needs and aspirations of the local population.
3. Continuous Improvement: By combining the strengths of both approaches, urban planners can create a dynamic and adaptive planning process that evolves as new data and insights become available.
In conclusion, AI-driven slum prediction algorithms and community input models offer complementary approaches to urban planning. By leveraging the strengths of each method and addressing their limitations, urban planners can create more inclusive, effective, and sustainable slum prevention strategies.