Introduction:
The emergence of lab-grown meat, also known as cellular agriculture, has sparked a revolution in the food industry. As consumers become increasingly health-conscious and environmentally aware, the demand for sustainable and ethical food options has surged. This article delves into the adoption of lab-grown meat, explores the concept of cellular agriculture, and provides cost parity projections by region.

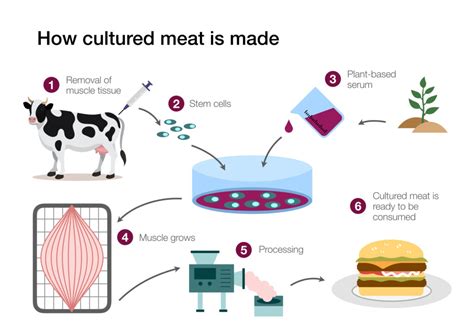
1. Lab-Grown Meat Adoption:
Lab-grown meat, derived from animal cells, offers a promising alternative to traditional meat production. The adoption of this innovative technology is gaining momentum globally, driven by several factors:
a. Health Benefits: Lab-grown meat is free from antibiotics, hormones, and other harmful substances often found in conventionally produced meat. This makes it an attractive option for health-conscious consumers.
b. Environmental Impact: Cellular agriculture significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions, land use, and water consumption compared to traditional meat production. This factor has played a crucial role in the adoption of lab-grown meat.
c. Ethical Considerations: The use of cellular agriculture eliminates the need for animal suffering, which appeals to consumers who are concerned about animal welfare.
2. Cellular Agriculture:
Cellular agriculture involves cultivating animal cells in a controlled environment to produce meat. This technology has several advantages over traditional meat production:
a. Scalability: Cellular agriculture can be scaled up or down to meet demand, ensuring a stable supply of lab-grown meat.
b. Customization: The process allows for the customization of meat products based on consumer preferences, such as flavor, texture, and nutritional content.
c. Reduction in Waste: Cellular agriculture minimizes waste generated during traditional meat production, such as offal and bone.
3. Cost Parity Projections by Region:
The cost of lab-grown meat is a significant factor influencing its adoption. Projections indicate that cost parity with conventionally produced meat is achievable in the near future, with variations across regions:
a. North America: Due to high labor costs and strong consumer demand, the cost parity for lab-grown meat in North America is expected to be achieved by 2025.
b. Europe: Europe is likely to reach cost parity by 2027, driven by increased investment in cellular agriculture research and development.
c. Asia: Asia, with its vast population and growing middle class, is expected to reach cost parity by 2030, as technological advancements and economies of scale contribute to lower production costs.
d. Latin America and Africa: These regions may take longer to reach cost parity, with projections estimating it to be achieved by 2035, driven by lower production costs and increasing consumer demand.
Conclusion:
The adoption of lab-grown meat, enabled by cellular agriculture, is poised to transform the food industry. As cost parity becomes a reality in various regions, the demand for sustainable and ethical food options is expected to soar. This shift in consumer preferences and the environmental benefits of lab-grown meat make it a compelling solution for a sustainable future.