Introduction:
The quantum internet, a revolutionary communication system, is poised to revolutionize the way we transmit information. Utilizing quantum entanglement, this technology promises to offer unprecedented levels of security, speed, and efficiency. This article delves into the timelines, entanglement distribution, and network rollout phases of the quantum internet.

1. Timelines:
The development of the quantum internet is a multi-decade endeavor that involves various stages. Here’s an overview of the key timelines:
a. Early research and development (1980s-1990s): The concept of quantum entanglement was first proposed, and scientists began to explore its potential applications in communication.
b. Quantum key distribution (QKD) and entanglement-based communication (2000s): The first practical QKD systems were developed, paving the way for secure communication. Researchers also started to experiment with entanglement-based communication.
c. Quantum internet research and pilot projects (2010s-2020s): Governments, universities, and private companies began investing in quantum internet research. Pilot projects and demonstrations started to emerge, showcasing the potential of the technology.
d. Commercial deployment and widespread adoption (2030s and beyond): The quantum internet is expected to become commercially viable and widely adopted by this time, offering a new level of communication infrastructure.
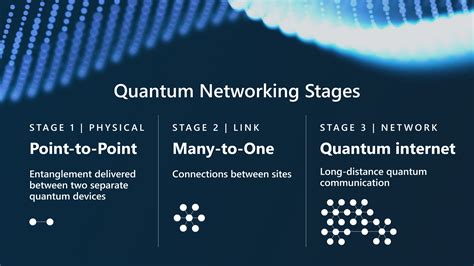
2. Entanglement Distribution:
The core of the quantum internet is the distribution of entangled particles, which enables quantum communication. Here are the key phases in entanglement distribution:
a. Ground-based entanglement distribution: Early efforts focused on creating entangled photons using laser sources. These photons were then transmitted through optical fibers, establishing the first quantum communication links.
b. Satellite-based entanglement distribution: To overcome the limitations of ground-based systems, researchers are exploring the use of quantum satellites. These satellites can create and distribute entangled particles over vast distances, facilitating long-distance quantum communication.
c. Quantum repeaters and entanglement swapping: To extend the range of quantum communication, quantum repeaters are being developed. These devices use entanglement swapping to create entangled particles between distant quantum networks.
3. Network Rollout Phases:
The rollout of the quantum internet involves several phases, each building upon the previous one:
a. Initial infrastructure deployment: This phase involves setting up the foundational components of the quantum network, such as quantum routers, repeaters, and optical fibers.
b. Expansion and interconnection: As the initial infrastructure is established, the network expands to include more nodes and interconnects with existing communication networks, such as the internet.
c. Integration with quantum computing and other technologies: The quantum internet will eventually integrate with quantum computing and other emerging technologies, creating a more comprehensive quantum ecosystem.
d. Widespread adoption and standardization: The final phase involves the widespread adoption of the quantum internet by various industries and the development of standards to ensure interoperability and security.
Conclusion:
The quantum internet is a transformative technology with the potential to revolutionize communication. By understanding the timelines, entanglement distribution, and network rollout phases, we can better appreciate the progress made and the challenges ahead in realizing this groundbreaking technology. As we move towards a future where quantum communication is commonplace, the quantum internet promises to reshape the way we share information, offering unparalleled security and efficiency.