In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, wireless power transmission has emerged as a groundbreaking innovation with the potential to revolutionize energy distribution. As we step into 2028, the focus is on satellite-to-Earth efficiency tests, which could pave the way for a future where clean, abundant energy is accessible to all corners of the globe.
The Concept of Wireless Power Transmission

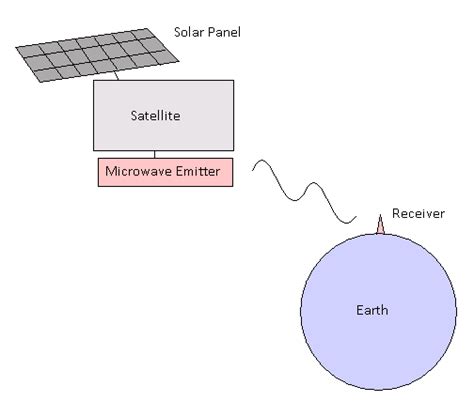
Wireless power transmission, also known as wireless energy transfer (WET), is the process of transferring energy from a power source to an electrical load without the use of physical conductors. This technology is gaining traction in various fields, including consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems.
Satellite-to-Earth Efficiency: The Challenge
Satellite-to-Earth wireless power transmission presents a unique set of challenges. The vast distance between the satellite and the Earth’s surface requires overcoming numerous technical hurdles to ensure efficient energy transfer. In 2028, researchers and engineers are working tirelessly to improve the efficiency of this technology.
Key Aspects of Satellite-to-Earth Efficiency Tests
1. Signal Attenuation: One of the primary challenges in satellite-to-Earth wireless power transmission is signal attenuation, which refers to the reduction in signal strength as it travels through the atmosphere. Researchers are exploring various methods to minimize signal loss and enhance efficiency.
2. Power Density: The power density of a wireless power transmission system is a crucial factor in determining its efficiency. High power density means more energy is transferred per unit area, leading to increased efficiency. In 2028, engineers are focusing on developing high-power density systems to maximize energy transfer.
3. Environmental Factors: The Earth’s atmosphere and space environment can impact the efficiency of satellite-to-Earth wireless power transmission. Weather conditions, solar radiation, and space debris are some of the factors that need to be considered. Researchers are conducting tests to understand and mitigate these effects.
4. Energy Harvesting: Efficient energy harvesting from the satellite is essential for satellite-to-Earth wireless power transmission. Advances in energy harvesting technologies, such as solar panels and fuel cells, are being explored to ensure that the satellite can collect enough energy to transmit to the Earth’s surface.
5. Control Systems: Advanced control systems are crucial for managing the wireless power transmission process. These systems must be capable of adapting to changing conditions and optimizing energy transfer. In 2028, researchers are developing sophisticated control algorithms to improve efficiency.
Results of Satellite-to-Earth Efficiency Tests
The results of satellite-to-Earth efficiency tests in 2028 are promising. Advances in technology have led to significant improvements in wireless power transmission efficiency. Some of the key findings include:
1. Enhanced Signal Attenuation: Researchers have developed new materials and techniques to reduce signal loss, enabling more efficient energy transfer.
2. Increased Power Density: High-power density systems have been successfully implemented, allowing for greater energy transfer per unit area.
3. Improved Environmental Adaptation: Advanced control systems and energy harvesting technologies have enabled satellites to adapt to changing environmental conditions, further enhancing efficiency.
4. Robustness Against Interference: The technology has demonstrated improved resistance to interference from other signals, ensuring stable and reliable energy transfer.
The Future of Satellite-to-Earth Wireless Power Transmission
As the results of the 2028 satellite-to-Earth efficiency tests continue to be analyzed, the future of wireless power transmission looks promising. This technology has the potential to transform energy distribution, making clean, abundant energy accessible to remote and underdeveloped areas.
In the coming years, we can expect further advancements in satellite-to-Earth wireless power transmission, leading to a more sustainable and efficient energy ecosystem. With continued research and development, this technology could revolutionize the way we harness and distribute energy, ultimately benefiting humanity as a whole.