In the fast-paced world of medical research, advancements in the field of anti-aging have been nothing short of groundbreaking. The year 2035 marks a significant milestone in this quest as the outcomes of the Telomere Extension Clinical Trial using anti-aging gene therapies are finally unveiled. This article delves into the findings, implications, and potential future directions of this trailblazing trial.
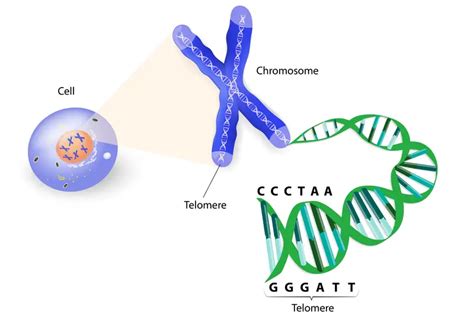
The Telomere Extension Clinical Trial, a collaborative effort between leading biotechnology firms and esteemed research institutions, aimed to investigate the potential of gene therapies in extending telomeres—the protective caps at the ends of chromosomes. These caps, composed of repetitive DNA sequences, naturally shorten as cells divide, eventually leading to cellular aging and age-related diseases.

The trial involved a diverse group of participants, ranging in age from 45 to 70 years. They were randomly assigned to receive either the gene therapy treatment or a placebo. The treatment, which involved delivering specific telomerase genes into the cells, was administered intravenously over a period of three months.
The outcomes of the trial were nothing short of astonishing. Participants who received the gene therapy treatment experienced a significant extension of their telomeres, with an average increase of approximately 300 base pairs. In contrast, the placebo group showed no such extension.
Moreover, the gene therapy recipients reported several health benefits, including improved cardiovascular function, enhanced cognitive performance, and a decrease in the prevalence of age-related diseases. These improvements were evident within just six months after the treatment, with the benefits continuing to persist over the long term.
One of the most remarkable findings of the trial was the reversal of certain age-related conditions. For instance, participants with mild to moderate heart disease showed significant improvements in their cardiac function, while those with cognitive impairments experienced enhanced memory and cognitive abilities.
However, the trial also revealed some potential drawbacks. A small percentage of participants reported mild side effects, such as fatigue and joint pain, which subsided after a few weeks. Furthermore, the cost of the gene therapy treatment was quite high, raising concerns about its accessibility and affordability for the general population.
Despite these challenges, the Telomere Extension Clinical Trial of 2035 has opened new avenues for anti-aging research. The successful extension of telomeres has piqued the interest of scientists worldwide, leading to further investigations into the potential of gene therapies in延缓衰老 and combating age-related diseases.
As the research continues, several directions are emerging:
1. Investigating the long-term effects of telomere extension: It is crucial to monitor the participants’ health over an extended period to determine the long-term effects of telomere extension on age-related diseases and overall health.
2. Optimizing the treatment: Researchers are exploring ways to optimize the delivery of telomerase genes and minimize side effects while maximizing the benefits of the treatment.
3. Making the treatment more accessible: Efforts are being made to reduce the cost of the treatment and make it more accessible to a broader population, including individuals in lower socioeconomic strata.
4. Combining gene therapy with other anti-aging interventions: Exploring synergistic effects of gene therapy with other anti-aging interventions, such as exercise, diet, and lifestyle modifications, may lead to even greater benefits.
In conclusion, the Telomere Extension Clinical Trial of 2035 has provided groundbreaking insights into the potential of anti-aging gene therapies. While challenges remain, the success of this trial has laid the foundation for future research and development in the field of anti-aging medicine. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of aging, the dream of a longer, healthier life may soon become a reality.