Introduction:
In recent years, the construction industry has witnessed a significant transformation with the integration of advanced technologies such as drones. Autonomous construction zones are now a reality, where drones play a crucial role in enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring safety. This article explores the coordination of drone swarms in autonomous construction zones and the safety protocols that govern their operations.

1. Drone Swarm Coordination:
1.1 Formation Flying:
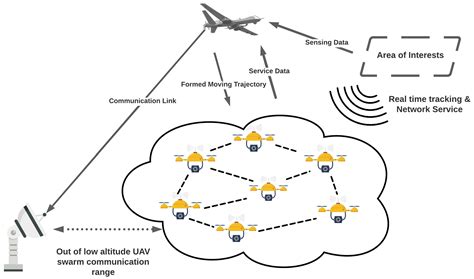
Drone swarms in autonomous construction zones are coordinated through formation flying techniques. This involves organizing the drones into specific formations that optimize their collective performance. Formation flying allows for efficient navigation, communication, and data collection, thereby improving the overall productivity of construction projects.
1.2 Task Allocation:
Task allocation is a critical aspect of drone swarm coordination. Each drone is assigned a specific task based on its capabilities and the project’s requirements. This ensures that the swarm operates effectively and avoids unnecessary collisions or interference. Advanced algorithms are employed to dynamically allocate tasks to drones, taking into account factors such as workload, distance, and energy levels.
1.3 Collision Avoidance:
Collision avoidance is a vital safety measure in drone swarm operations. Advanced sensors, such as LiDAR and cameras, are used to detect nearby obstacles and other drones. Real-time algorithms process this data to ensure that the drones maintain safe distances and avoid collisions. Additionally, adaptive control systems can adjust the drones’ flight paths to accommodate sudden changes in the environment.
2. Safety Protocols:
2.1 Regulatory Compliance:
Drone operations in autonomous construction zones must comply with local regulations and standards. This includes obtaining necessary permits, adhering to flight restrictions, and ensuring that the drones meet safety and performance requirements. Compliance with regulations minimizes legal risks and fosters public trust in drone technology.
2.2 Security Measures:
Security is a paramount concern in autonomous construction zones. Drones are susceptible to hacking and unauthorized access, which can lead to accidents or theft of sensitive data. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures, such as encryption and authentication protocols, is crucial to protect against potential threats. Regular security audits and updates are essential to maintain a secure environment.
2.3 Emergency Protocols:
In the event of a drone failure or other unforeseen circumstances, emergency protocols must be in place to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment. This includes immediate grounding of the affected drones, conducting on-site investigations, and implementing corrective measures to prevent future incidents. Regular training and drills are conducted to ensure that all personnel are prepared for emergency situations.
Conclusion:
The integration of drone swarms in autonomous construction zones offers numerous benefits, including increased efficiency and safety. Effective coordination of drone swarms, coupled with stringent safety protocols, is essential to harness the full potential of this technology. As the construction industry continues to evolve, it is crucial to stay abreast of advancements in drone technology and ensure that safety remains a top priority.