Introduction:
The field of quantum biology has been witnessing remarkable advancements in recent years. One of the most intriguing applications of quantum computing in biology is the prediction of protein folding, a fundamental process in cellular life. In this article, we delve into the potential of qubit-enhanced simulations for protein folding prediction in the year 2028.

1. The Significance of Protein Folding:
Protein folding is a complex process where a linear chain of amino acids arranges itself into a three-dimensional structure. This structure determines the protein’s function within a living organism. However, predicting the correct folding pathway and structure of a protein remains a significant challenge in biology.
2. Traditional Protein Folding Prediction Methods:
Conventional methods for protein folding prediction rely on computational algorithms and databases. These methods have made significant progress, but they still struggle with the vast conformational space and the intricate nature of protein folding.
3. The Emergence of Quantum Computing:
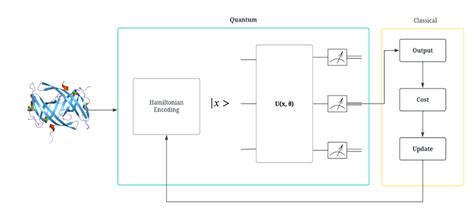
Quantum computing, with its ability to process vast amounts of data simultaneously, holds the promise of revolutionizing protein folding prediction. By harnessing the power of qubits, quantum computers can perform complex calculations that are beyond the reach of classical computers.
4. Qubit-Enhanced Simulations:
Qubit-enhanced simulations leverage the principles of quantum mechanics to model the folding process of proteins. These simulations aim to provide a more accurate and efficient prediction of protein structures and pathways.
5. Advancements in Quantum Biology 2028:
By 2028, the field of quantum biology is expected to witness several advancements in protein folding prediction using qubit-enhanced simulations:
a. Improved Quantum Algorithms: Quantum algorithms specifically designed for protein folding prediction will be more efficient and accurate. These algorithms will take advantage of the inherent parallelism of quantum computers to explore the vast conformational space of proteins.
b. Enhanced Qubit Quantum Coherence: Quantum computers will have better qubit coherence, enabling longer simulations and more accurate predictions. This will lead to a deeper understanding of the folding process and its underlying mechanisms.
c. Integration with Classical Computing: Quantum computers will be integrated with classical computing resources, allowing for a hybrid approach to protein folding prediction. This hybrid approach will combine the strengths of both classical and quantum computing, leading to faster and more accurate predictions.
6. Potential Applications:
The advancements in protein folding prediction using qubit-enhanced simulations will have numerous applications in the field of biology, including:
a. Drug Discovery: Accurate protein folding predictions can aid in the design of novel drugs and the optimization of existing ones. This can lead to more effective treatments for diseases like cancer, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s.
b. Biotechnology: Understanding the folding process of proteins can help in the development of new biotechnological applications, such as the production of biofuels, pharmaceuticals, and enzymes.
c. Bioinformatics: Improved protein folding predictions can enhance the analysis of biological data, leading to a better understanding of cellular processes and the development of new computational tools.
Conclusion:
Quantum biology in the year 2028 will witness significant advancements in protein folding prediction using qubit-enhanced simulations. These advancements will revolutionize the field of biology, leading to new discoveries and applications that can improve human health and the quality of life. As quantum computing continues to evolve, the potential of qubit-enhanced simulations for protein folding prediction will only grow, paving the way for a new era in biology.