Introduction:
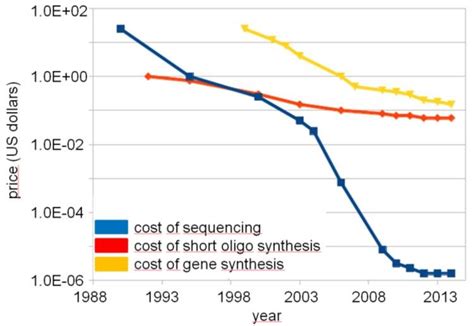
Synthetic biology, a rapidly evolving field, is revolutionizing the way we understand and manipulate living systems. As technology advances, the cost of DNA synthesis continues to decline, making it more accessible for researchers and entrepreneurs. In this article, we explore the potential trends in the cost per base pair for DNA printers in synthetic biology foundries by the year 2030.

1. Technological Advancements in DNA Synthesis
Over the past few years, there have been significant breakthroughs in DNA synthesis technology. These advancements include improvements in DNA synthesis reactions, novel base analogs, and optimized reaction conditions. These innovations are expected to further decrease the cost of synthesizing DNA.
1.1. High-Fidelity Enzymes:
High-fidelity enzymes have revolutionized DNA synthesis by reducing the error rate during the process. These enzymes are highly specific and can produce longer DNA sequences with minimal errors. As the cost of producing these enzymes decreases, the overall cost of DNA synthesis will follow suit.
1.2. Continuous Flow Chemistry:
Continuous flow chemistry allows for the synthesis of long DNA sequences by continuously adding reactants and removing by-products. This technique reduces the need for purification steps, thereby lowering the cost per base pair.
2. Economies of Scale and Industry Collaboration
The cost of DNA synthesis is likely to decline as economies of scale come into play and industry collaboration increases. Here are some factors that will contribute to this trend:
2.1. Foundry Model:
Synthetic biology foundries, which offer DNA synthesis services, can leverage economies of scale by synthesizing large volumes of DNA. This model encourages cost-sharing among customers and promotes competitive pricing.
2.2. Collaborations between Foundries and Technology Companies:
As technology companies develop more efficient DNA synthesis methods, foundries can integrate these technologies into their production processes. This collaboration will lead to further cost reductions.
3. Competition in the Market
The increasing competition in the DNA synthesis market will also contribute to a decrease in the cost per base pair. Here are a few key players in the market:
3.1. Twist Bioscience:
Twist Bioscience has developed a novel semiconductor-based DNA synthesis platform that can produce high-quality DNA at a lower cost. The company’s focus on high-throughput production is expected to drive down costs further.
3.2. GENEWIZ:
GENEWIZ is one of the leading providers of DNA synthesis services. The company’s extensive experience in the field has enabled it to optimize its production processes, resulting in competitive pricing.
3.3. Oxford Nanopore Technologies:
Oxford Nanopore Technologies is developing a novel DNA synthesis platform that can produce long DNA sequences at a low cost. This platform is expected to disrupt the market and drive down prices.
Conclusion:
The cost per base pair for DNA printers in synthetic biology foundries is expected to decline significantly by 2030. Advances in technology, economies of scale, industry collaboration, and competition in the market will all contribute to this trend. As costs continue to fall, the accessibility of DNA synthesis will expand, opening new avenues for research and innovation in synthetic biology.