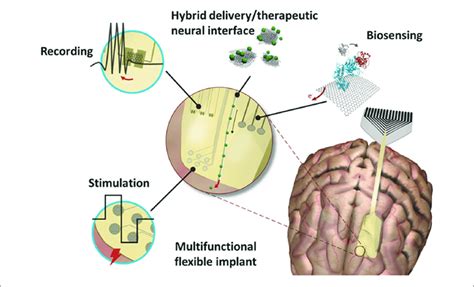
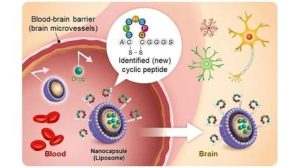
In the rapidly evolving field of neuroscience, one of the most promising areas of research is the development of neural lace interfaces. These interfaces involve the integration of a mesh-like structure, often made of graphene, directly into the brain’s cortex to enable direct communication between the brain and external devices. This article delves into the intricacies of graphene mesh cortical integration and explores the safety timelines associated with this cutting-edge technology.
**Graphene Mesh Cortical Integration**

Graphene, a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, is renowned for its exceptional electrical conductivity, flexibility, and strength. These properties make it an ideal material for neural lace interfaces. The concept involves the insertion of a mesh-like structure of graphene into the brain’s cortex, which allows for seamless communication between neural cells and external devices.
The process of integrating the graphene mesh into the cortex is typically minimally invasive, often requiring a small incision in the scalp. Once the mesh is in place, it forms a direct electrical connection with the brain cells, facilitating the transfer of information.
**Safety Considerations**
The safety of neural lace interfaces is a crucial aspect of their development. Researchers and engineers must address several concerns to ensure the technology is safe for human use:
1. **Biocompatibility:** The graphene mesh must be biocompatible, meaning it does not cause any adverse reactions or inflammation in the brain tissue. Extensive testing has been conducted to ensure that graphene is safe for use in the brain.
2. **Immune Response:** The body’s immune system might react to the presence of the graphene mesh. Researchers are continuously working on developing coatings or materials that can minimize the immune response.
3. **Long-term Stability:** One of the biggest challenges is ensuring the long-term stability of the graphene mesh within the brain. The mesh must remain functional and integrate with the brain without causing any damage or degradation over time.
4. **Safety Timelines**
Safety timelines for neural lace interfaces are crucial to ensure that the technology is thoroughly tested before it is used in human subjects. The following milestones provide a general timeline for the development and safety evaluation of graphene mesh cortical integration:
– **Preclinical Testing:** This involves extensive testing on animals to evaluate the biocompatibility, immune response, and long-term stability of the graphene mesh. This phase may take several years.
– **Clinical Trials:** Once preclinical testing is successful, the next step is to conduct clinical trials on human volunteers. These trials are designed to further assess the safety and efficacy of the technology.
– **Regulatory Approval:** After clinical trials, the technology must be reviewed and approved by regulatory authorities such as the FDA. This process may take several years, depending on the results of the clinical trials.
**Conclusion**
Neural lace interfaces, utilizing graphene mesh cortical integration, hold immense potential for improving human lives. As researchers and engineers continue to address safety concerns and refine the technology, we can look forward to a future where direct brain-computer interfaces become a reality. The safety timelines for this technology are a testament to the rigorous approach required to ensure the well-being of individuals who may benefit from this groundbreaking advancement.